SpMet®Methemoglobin
Methemoglobin (SpMet®) is a breakthrough measurement that allows clinicians to noninvasively and immediately detect elevated levels of methemoglobin in the blood—facilitating earlier diagnosis and treatment for patients with methemoglobinemia, a dangerous but underdiagnosed and undertreated condition.

Click here to receive more information about Noninvasive
and Continuous Methemoglobin (SpMet®) »
Addressing the Risk of Dangerous Drug Reactions
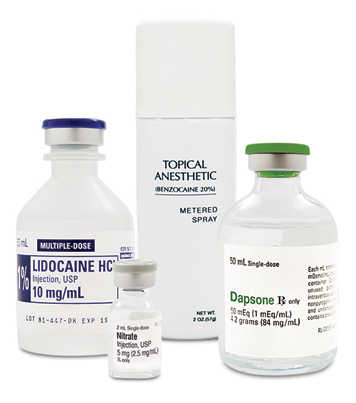
- > Many drugs commonly used in hospitals–such as lidocaine, benzocaine, dapsone, and nitrates–cause a dangerous reaction known as acquired methemoglobinemia.
- • Reduces oxygen delivery to tissues
- • Can occur in all care areas / patients
- • Often unrecognized and undiagnosed
- > While methemoglobinemia can occur in all care areas and patients, it is often unrecognized and undiagnosed.
- > If not detected and treated immediately, it can result in avoidable injury or death.
Medications Known to Cause Methemoglobinemia:
Benzocaine, Cetacaine, Chloroquine, Dapsone, EMLA topical, Flutamide, Lidocaine, Metoclopramide, Nitrates, Nitric oxide, Nitroglycerin, Nitroprusside, Nitrous oxide, Phenazopyridine (Pyridium), Prilocaine, Primaquine, Riluzole, Silver nitrate, Sodium nitrate, Sulfonamides.
Enabling Quick Treatment with SpMet
- > Masimo noninvasive methemoglobin (SpMet) helps clinicians assess for methemoglobinemia, facilitating earlier detection and immediate treatment to reduce patient risk—especially in care areas where drugs that cause methemoglobinemia are used most often, such as procedure labs and the operating room.
- > This enables them to quickly adjust exposure to the dangerous drug and initiate potentially life-saving treatment.
Prevalence of Methemoglobinemia
| Number of Methemoglobinemia Cases | Patient Age | Care Areas | Fatalities |
| 138 (2.5 cases per hospital per month) |
4 days to 86 years | Surgery, intensive care, outpatient clinics, pediatrics, emergency department, cardiac cath lab |
1 fatality 3 near fatalities |
Results from a retrospective study at two Johns Hopkins Hospitals over a 28-month period, using laboratory CO-Oximeter results, and patient electronic medical records.1
"Masimo SpMet helps detect methemoglobinemia, allowing clinicians to accurately diagnose and treat this life-threatening condition."
Mark Macknet, MD
Assistant Professor of Anesthesiology,
Loma Linda University
Loma Linda, CA
"Acquired Methemoglobinemia is fairly common and causes morbidity and mortality in both the inpatient and outpatient settings. Acquired methemoglobinemia is often unrecognized and thus untreated."
Dr. Rachel Ash-Bernal
and other researchers at Johns Hopkins Hospital
Technology Platform
Masimo rainbow® is a noninvasive monitoring platform enabling the assessment of multiple blood constituents and physiologic parameters that previously required invasive or complicated procedures, in addition to providing Masimo SET® Measure-through Motion and Low Perfusion™ pulse oximetry.
- > Total Hemoglobin (SpHb®)
- > Carboxyhemoglobin (SpCO®)
- > Methemoglobin (SpMet®)
- > Oxygen Content (SpOC™)
- > Acoustic Respiration Rate (RRa™)
- > Oxygen Saturation (SpO2)
- > Pulse Rate (PR)
- > Perfusion Index (PI)
- > Pleth Variability Index (PVI®)
The upgradeable rainbow® platform lets you choose the rainbow® measurements that are right for you now and be confident that your investment in patient safety won’t become obsolete tomorrow.
PDF Resources
 |
Data Sheet SpMet |
REFERENCES
- 1 Ash-Bernal RA et al. Medicine. 2004;83:265-273.






